Emissions bounced back in 2021, when people started resuming some of their normal activities, but offices have never been the same. While remote work was rare before the pandemic, today, 28 percent of Americans are working a “hybrid” schedule, going into the office some days, and 13 percent are working remotely full-time.
Recent data suggest that remote work could speed along companies’ plans to zero out their carbon emissions, but businesses don’t seem to be considering climate change in their decisions about the future of office work. “In the U.S., I’m sad to say it’s just not high on the priority list,” said Kate Lister, the founder of the consulting firm Global Workplace Analytics. “It gets up there, and then it drops again for the next shiny object.” Commuter travel falls under a company’s so-called “Scope 3” emissions, the indirect sources that routinely get ignored, but represent, on average, three-quarters of the business world’s emissions.
A 10 percent increase in people working remotely could reduce carbon emissions by 192 million metric tons a year, according to a study published in the journal Nature Cities earlier this month. That would cut emissions from the country’s most polluting sector, transportation, by 10 percent. Those findings align with other peer-reviewed research: Switching to remote work instead of going into the office can cut a person’s carbon footprint by 54 percent, according to a study published in the journal PNAS last fall, even when accounting for non-commute travel and residential energy use.
“It seems like a very obvious solution to a very pressing and real problem,” said Curtis Sparrer, a principal and co-founder of the PR agency Bospar, a San Francisco-based company where employees have been working remotely since it started in 2015. “And I am concerned that this whole ‘return-to-office’ thing is getting in the way.”
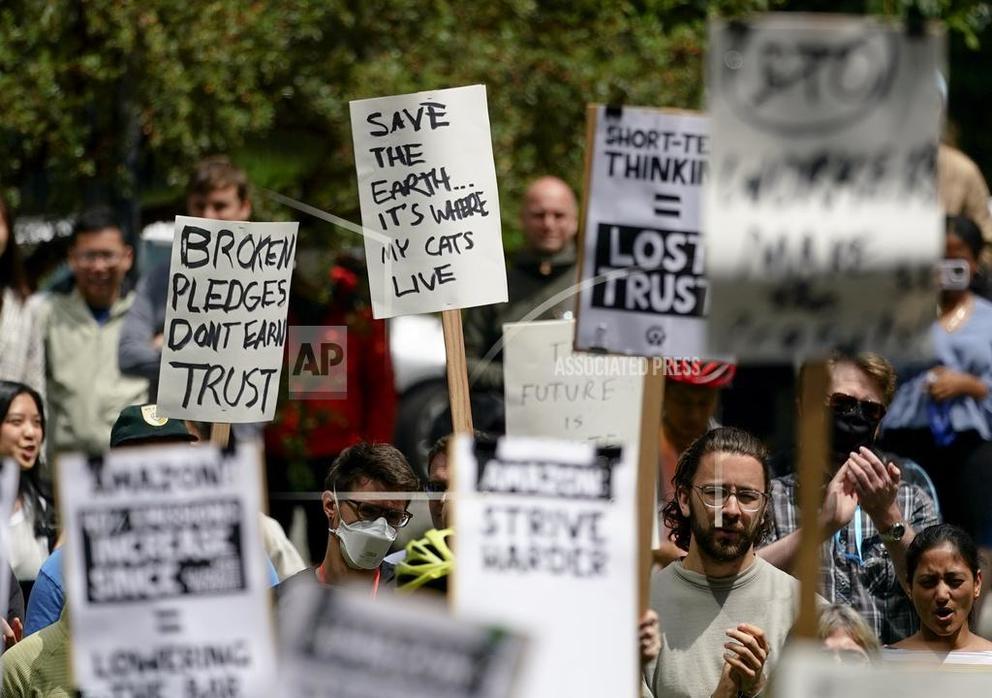
Many companies are mandating their employees show up for in-person work regularly. Last year, big tech companies like Google, Amazon, and Meta told employees that they had to come back to the office three days a week or face consequences, like a lower chance of getting promoted. Even Zoom, the company that became a household name during the pandemic for its video conferencing platform, is making employees who live within 50 miles of the office commute two days a week.
Of course, there are many benefits that come with heading into the office to work alongside other humans. Interacting with your coworkers in person gives you a social boost (without the awkward pauses in Zoom meetings) and a compelling reason to change out of your sweatpants in the morning. From a climate change standpoint, the problem is that most Americans tend to jump in their cars to commute, instead of biking or hopping on the bus. A recent poll from Bospar found that two-thirds of Americans are driving to work — and they’re mostly in gas-powered cars. Even though purchases of electric vehicles are rising, they make up roughly 1 percent of the cars on the road.
The climate benefits start falling off quickly when people are summoned into the office. Working from home two to four days a week cuts emissions by between 11 and 29 percent compared with full-time office work, according to the study in PNAS by researchers at Cornell University and Microsoft. If you only work remotely one day a week, those emissions are only trimmed by 2 percent. Another big factor is that maintaining physical office space sucks up a lot of energy, since it needs to be heated and cooled.
So should companies be allowed to claim they’re going green when they’re forcing employees to commute? Many Americans don’t think so, according to Bospar’s survey. Well over half of Millennials and Gen Zers said it’s hypocritical for companies to observe Earth Day while requiring employees to attend work in person.
Sparrer points to Disney, which celebrated Earth Month in April with a campaign to promote its environmental efforts but ordered workers to come into the office four days a week last year. Nike, meanwhile, promoted its Earth Day collection of “sustainable” leather shoes while its CEO, John Donahoe, argued that remote work stifled creativity. “In hindsight, it turns out, it’s really hard to do bold, disruptive innovation, to develop a boldly disruptive shoe on Zoom,” he told CNBC earlier this month.
“We are entering a time of magical thinking, where people seem to think that this is enough, and it’s not,” Sparrer said. “And the frustration I have is that we all got to experience what it’s like to work from home, and we know how it works, and we know how it can be improved.”
Working from home, though, could present its own environmental challenges. Recent research that looked at trends before the pandemic found that if 10 percent of the workforce started working remotely, transit systems in the U.S. would lose $3.7 billion every year, a 27 percent drop in fare revenue, according to the study in Nature Cities, conducted by researchers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, the University of Florida, and Peking University in Beijing. Some experts worry that remote work could push people into the suburbs, where carbon footprints tend to be higher than in cities.
Right now, there are many employees who want to work at home full-time but are forced to go into the office, Lister said. She sees the return-to-office mandates as a result of corporate leadership that wants to go back to how things used to be. “As that generation retires,” she said, “I think that a lot of these conversations will go away.”
This article originally appeared in Grist at https://grist.org/economics/return-to-office-carbon-emissions-remote-wo… Grist is a nonprofit, independent media organization dedicated to telling stories of climate solutions and a just future. Learn more at Grist.org